25 Difference in Electrodes Used Between Continuous Heartrate and a Routine Ekg
How to Place the Electrocardiogram Electrodes
The electrocardiogram electrodes are the devices which connect the patient to the electrocardiograph. The electrical data of the heart is obtained through them for the tracing and printing of the electrocardiogram.
For a standard electrocardiogram 10 electrodes are used, divided in two groups: limb electrodes and precordial electrodes. The 12 electrocardiogram leads are obtained from all data provided by them.
When an electrocardiogram is taken is essential to know the exact placement of the electrodes on the patient. Electrode misplacement could mean from small variations in QRS morphology to critical diagnostic errors.
EKG Electrodes Placement
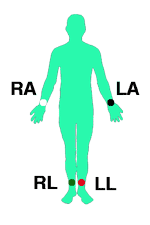
Limb Electrodes:
The four limb electrodes should be located on the arms and legs distal to the shoulders and hips1.
They are usually differentiated with a different color for each one (read tips for placing EKG electrodes).
- RA: right arm.
- LA: left arm.
- LL: left leg.
- RL: right leg (ground).
In the case of a patient with an amputated limb, the corresponding electrode will be placed on the residual limb, or failing this, on the nearest region of the torso (shoulders or lower abdominal region).
Precordial Electrodes:
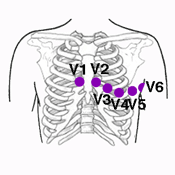
The six precordial electrodes are located on the precordial region2.
- V1: in the fourth intercostal space, just to the right of the sternum.
- V2: in the fourth intercostal space, just to the left of the sternum.
- V3: on a line midway between electrodes V2 and V4.
- V4: in the fifth intercostal space, in the mid-clavicular line.
- V5: at the same level as electrode V4, in the left anterior axillary line.
- V6: at the same level as electrodes V4 and V5, in the left midaxillary line.
In the article tips for placing electrocardiogram electrodes we show you how to avoid frequent mistakes.
Electrodes for Right-Side and Posterior Leads
In certain patients, in case of suspicion of posterior or right ventricle myocardial infarction, it is advisable to place the electrodes in positions other than described to obtain the posterior and right-sided leads.
Remember: electrodes should not be confused with leads. Electrodes refer to the devices we place on the patient and leads refer to the tracing of the electrical activity on the electrocardiogram.
In the next section we will further explain electrocardiogram leads. Click on next down below to stay with us. How to perform an electrocardiogram might also be of interest.
previous | next
References
- 1. Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G et Al. ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. European Heart Journal Nov 2014, 35 (43) 3033-3073.
- 2. Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou's electrocardiography in clinical practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elservier; 2008.
If you Like it... Share it.
Can't Miss
MOST POPULAR
Topics
Initial concepts
- Cardiac conduction system
- Cardiac cycle
- Coronary arteries
Basic principles
- Basic principles
- How to do an EKG
- EKG paper
- Electrodes
- Tips EKG electrodes
- Electrode color coding
- EKG leads
- Right-side and posterior
- EKG waves
- The Q wave
- The U wave
- Intervals and segments
- Locating walls
- QRS morphology
Read an EKG
- Read an EKG
- Heart rate
- Heart rhythm
- Normal sinus rhythm
- PR interval
- QT interval
- Heart axis
- Right-axis deviation
- Left-axis deviation
- Extreme axis deviation
- ST-segment
- Abnormal waves
Arrhythmias
- Arrhythmias
- Sick sinus syndrome
- Sinus arrhythmia
- AV blocks
- 1st degree AV block
- 2nd degree AV block
- 3th degree AV block
- Atrial flutter
- Atrial fibrillation
- Supraventricular tach.
- AVNRT
- Inappr. sinus tach.
- Pre-excitation synd.
- Ventricular arrhythmias
- PVCs
- Ventricular tachycardias
- VT criteria
- Torsades de pointes
- Fascicular left VT
- Ashman phenomenon
Bundle branch blocks
- Bundle branch blocks
- Right BBB
- Incomplete RBBB
- Left BBB
- Incomplete LBBB
- Left hemiblocks
- Bifascicular blocks
Ischemia
- Ischemic heart disease
- Chest pain and EKG
- Ischemia, injury and infarction
- Acute coronary syndromes
- NSTE-ACS
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Atypical presentations
- Occluded artery
- Modified Sgarbossa criteria
Hypertrophy & dilation
- Left atrial enlargement
- Right atrial enlargement
- Left ventricular hypertrophy
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
- Sokolow-Lyon criteria
Metabolic & drugs
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Digoxin
- Hydroxychloroquine
Pacemaker
- Pacemaker & EKG
- Read an EKG with pacemaker
- Pacemaker nomenclature
- Pacemaker malfunction
Pediatric EKG
- Pediatric EKG
- Read a pediatric EKG
- Atrial septal defect
- Ventricular septal defects
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Pulmonary stenosis
Other articles
- Pericarditis
- Early repolarization
- Brugada syndrome
- Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy
- Bayés syndrome
- Dressler syndrome
- Pulmonary embolism
- Hypothermia
- Pregnancy
- Normal EKG in athletes
- Abnormal EKG in athletes
Calculations
- Heart axis
- Heart rate
- CHA2DS2-Vasc
- Corrected QT
- Romhilt-Estes
- R-R interval
- Aortic valve
Source: https://en.my-ekg.com/basic-principles/electrodes-ekg.html
0 Response to "25 Difference in Electrodes Used Between Continuous Heartrate and a Routine Ekg"
Publicar un comentario